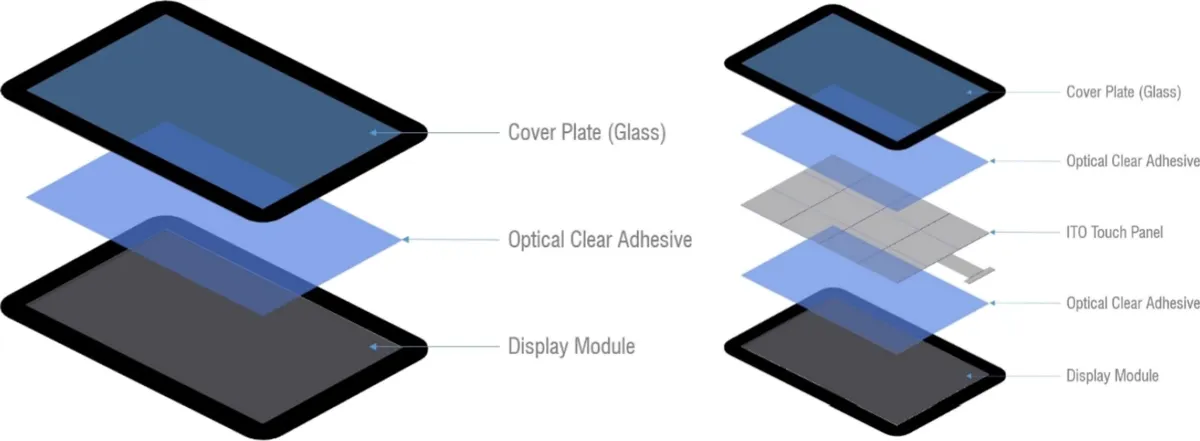
Touchscreen technology has revolutionized medical device interfaces, enabling healthcare professionals to interact with complex medical equipment more intuitively and efficiently. This comprehensive guide explores how touchscreen technology is applied in medical devices, examining the unique requirements, challenges, and benefits of touch interfaces in healthcare environments. From patient monitoring systems to surgical equipment, discover how touchscreens are transforming medical device usability and patient care.
Medical device manufacturers face unique challenges when integrating touchscreen technology into healthcare equipment. These devices must meet stringent regulatory requirements, support gloved operation, withstand frequent disinfection, and provide reliable performance in critical care situations. Touchscreen interfaces in medical devices must balance advanced functionality with simplicity and safety.
The adoption of touchscreen technology in medical devices has accelerated in recent years, driven by the need for more intuitive interfaces, improved workflow efficiency, and better integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems. Understanding how touchscreens are implemented in medical applications helps healthcare facilities make informed technology decisions.
Unique Requirements for Medical Touchscreens
Medical device touchscreens must meet specific requirements that differ significantly from consumer or commercial applications. These requirements ensure patient safety, infection control, and reliable operation in clinical environments.
Critical Requirements
- Gloved Operation: Must function reliably with medical gloves (latex, nitrile, vinyl)
- Disinfection Compatibility: Resistant to harsh cleaning chemicals and frequent disinfection
- Regulatory Compliance: Must meet FDA, CE marking, and other medical device regulations
- High Reliability: Critical for patient safety - no failures during operation
- EMI/EMC Compliance: Must not interfere with other medical equipment
- Water and Fluid Resistance: Protection against spills and contamination
- Brightness and Readability: Clear visibility in various lighting conditions

Patient Monitoring Systems
Patient monitoring systems are among the most critical applications of touchscreen technology in healthcare. These systems display vital signs, alarms, and patient data, requiring intuitive interfaces for quick access to critical information.
Applications in Patient Monitoring
- Vital Signs Monitors: Touchscreen interfaces for viewing and configuring heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and temperature
- ICU Monitoring: Large format touch displays for multi-patient monitoring in intensive care units
- Anesthesia Workstations: Touch-enabled control panels for anesthesia delivery and monitoring
- Fetal Monitors: Touch interfaces for obstetric monitoring during labor and delivery
- Telemetry Systems: Remote patient monitoring with touchscreen displays for data review
Key Features
- Quick access to alarm settings and thresholds
- Intuitive navigation through patient data and trends
- Multi-patient view capabilities on large displays
- Integration with hospital information systems
- Customizable display layouts for different care settings
Diagnostic Imaging Equipment
Touchscreen technology has transformed diagnostic imaging equipment interfaces, making complex imaging systems more accessible and easier to operate. Radiologists and technicians can interact with imaging data more intuitively through touch interfaces.
Imaging Equipment Applications
- Ultrasound Systems: Touchscreen controls for probe selection, imaging modes, and measurement tools
- X-Ray Systems: Touch interfaces for exposure settings, image review, and patient positioning
- MRI and CT Scanners: Touch-enabled control panels for scan protocols and image reconstruction
- Endoscopy Systems: Touchscreen interfaces for camera control and image capture
- PACS Workstations: Touch displays for viewing and manipulating medical images
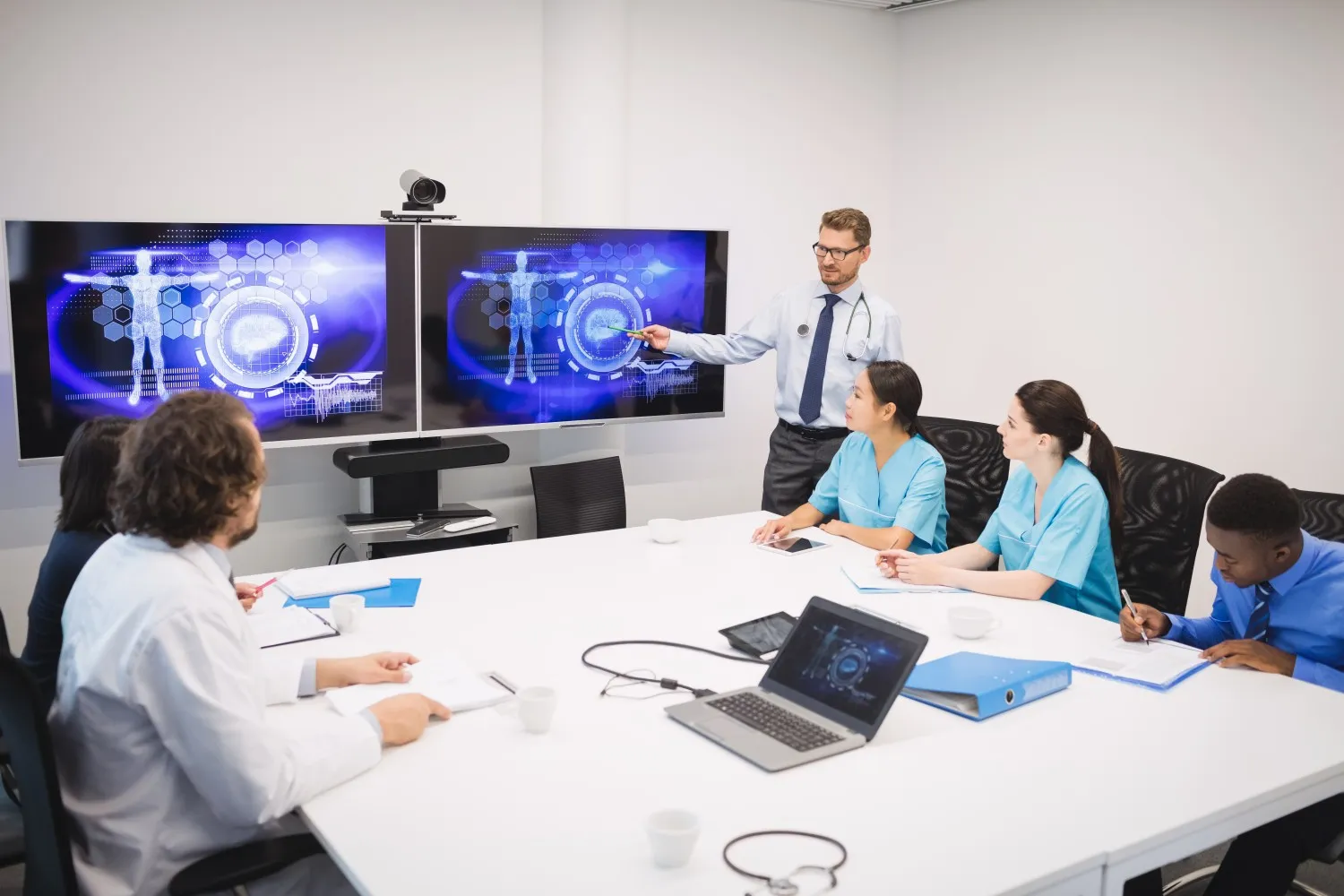

Benefits in Imaging
- Faster workflow with intuitive touch gestures
- Improved image manipulation with multi-touch capabilities
- Reduced training time for new operators
- Better integration with DICOM and PACS systems
- Enhanced ergonomics compared to traditional controls
Laboratory Equipment
Laboratory analyzers and diagnostic equipment increasingly feature touchscreen interfaces for sample processing, result review, and quality control. Touchscreens streamline laboratory workflows and reduce the potential for errors.
Laboratory Applications
- Blood Analyzers: Touchscreen interfaces for sample loading, test selection, and result review
- Chemistry Analyzers: Touch-enabled controls for reagent management and calibration
- Microbiology Systems: Touch interfaces for culture identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing
- Molecular Diagnostics: Touchscreen controls for PCR and sequencing equipment
- Hematology Analyzers: Touch displays for blood cell counting and analysis
Laboratory-Specific Requirements
- Resistance to chemical spills and contamination
- Easy cleaning and decontamination
- Support for barcode scanning integration
- LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System) connectivity
- Audit trail capabilities for regulatory compliance
Surgical and Operating Room Equipment
Surgical equipment with touchscreen interfaces must meet the highest standards for sterility, reliability, and ease of use. Touch interfaces in the operating room enable surgeons and staff to control equipment without breaking sterile fields.
Surgical Applications
- Surgical Displays: Touch-enabled monitors for viewing surgical images and patient data
- Electrosurgical Units: Touchscreen controls for power settings and mode selection
- Endoscopic Systems: Touch interfaces for camera control and image management during surgery
- Patient Positioning Systems: Touchscreen controls for operating table adjustments
- Surgical Navigation: Touch displays for image-guided surgery systems
Operating Room Considerations
- Sterile operation requirements
- Voice control integration as alternative to touch
- High brightness for visibility in bright OR lighting
- Minimal reflection and glare
- Rapid response for time-critical operations
Patient Registration and Check-In Systems
Touchscreen kiosks for patient registration and check-in have become common in hospitals and clinics, reducing wait times and improving the patient experience while freeing staff for other tasks.
Registration Applications
- Self-Service Kiosks: Touchscreen terminals for patient check-in and information updates
- Appointment Scheduling: Touch interfaces for scheduling and rescheduling appointments
- Insurance Verification: Touch-enabled systems for insurance card scanning and verification
- Payment Processing: Touchscreen interfaces for co-pay and bill payment
- Wayfinding Systems: Interactive touch displays for navigation within healthcare facilities
Benefits
- Reduced wait times and improved patient flow
- Decreased administrative burden on staff
- Improved data accuracy through direct patient input
- 24/7 availability for after-hours registration
- Multi-language support for diverse patient populations
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems
Touchscreen interfaces have transformed how healthcare providers interact with electronic health records. Tablet-based EHR systems with touch interfaces enable point-of-care documentation and improve workflow efficiency.
EHR Applications
- Tablet-Based Documentation: Touchscreen tablets for bedside charting and note entry
- Clinical Decision Support: Touch interfaces for accessing clinical guidelines and drug information
- Order Entry Systems: Touch-enabled interfaces for medication and test ordering
- Patient Portals: Touchscreen kiosks for patients to access their health records
- Mobile Workstations: Touch-enabled carts for EHR access throughout the facility

EHR Touchscreen Benefits
- Faster documentation compared to keyboard entry
- Improved mobility and flexibility for clinicians
- Better patient engagement during documentation
- Reduced transcription errors
- Integration with barcode scanning and other peripherals
Pharmacy and Medication Management
Touchscreen technology plays a crucial role in pharmacy operations and medication management systems, improving accuracy and efficiency in medication dispensing and administration.
Pharmacy Applications
- Automated Dispensing Cabinets: Touchscreen interfaces for medication retrieval and inventory management
- Pharmacy Information Systems: Touch-enabled workstations for prescription processing
- Medication Administration: Touchscreen interfaces on medication carts and pumps
- IV Pump Programming: Touch controls for infusion rate and volume settings
- Barcode Medication Administration: Touch displays integrated with barcode scanning systems
Safety Features
- Drug interaction checking and alerts
- Dosage calculation and verification
- Patient identification confirmation
- Audit trails for medication administration
- Integration with pharmacy information systems
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Touchscreen technology enables telemedicine applications, allowing remote consultations and patient monitoring through intuitive touch interfaces on tablets and specialized medical devices.
Telemedicine Applications
- Video Consultation Systems: Touchscreen tablets for telemedicine appointments
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Touch interfaces on home monitoring devices
- Mobile Health Apps: Touchscreen interfaces for patient self-monitoring
- Tele-ICU Systems: Touch-enabled displays for remote intensive care monitoring
- Wearable Health Devices: Touch interfaces on smart health monitors and fitness trackers
Touchscreen Technology Selection for Medical Devices
Selecting the appropriate touchscreen technology for medical devices requires careful consideration of the specific application requirements and environmental conditions.
| Medical Application | Recommended Technology | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Monitors | Resistive or Projected Capacitive | Gloved operation, easy cleaning, high reliability |
| Imaging Equipment | Projected Capacitive | Multi-touch, high resolution, gesture support |
| Laboratory Analyzers | Resistive | Chemical resistance, gloved operation, easy disinfection |
| Surgical Equipment | Resistive | Sterile operation, high reliability, gloved use |
| EHR Tablets | Projected Capacitive | Multi-touch, portability, long battery life |
| Patient Kiosks | Projected Capacitive or Infrared | Public use, durability, multi-touch |
| Pharmacy Systems | Resistive | Gloved operation, easy cleaning, reliability |
| Telemedicine Devices | Projected Capacitive | Portability, multi-touch, video support |
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Medical device touchscreens must comply with various regulatory requirements to ensure patient safety and device effectiveness.
Key Regulatory Requirements
- FDA Approval: Medical devices with touchscreens must meet FDA requirements for safety and effectiveness
- CE Marking: Compliance with European Medical Device Regulation (MDR)
- IEC 60601: Medical electrical equipment safety standards
- ISO 13485: Quality management systems for medical devices
- HIPAA Compliance: Protection of patient health information on touchscreen devices
- EMC Standards: Electromagnetic compatibility to prevent interference with other medical equipment
Design Considerations for Medical Touchscreens
Effective medical device touchscreen design requires careful attention to usability, safety, and clinical workflow integration.
Usability Design Principles
- Large Touch Targets: Buttons and controls sized for gloved operation (minimum 44x44 pixels)
- Clear Visual Feedback: Immediate response to touch input with visual and haptic feedback
- Intuitive Navigation: Logical menu structures and consistent interaction patterns
- Error Prevention: Confirmation dialogs for critical actions, undo capabilities
- Accessibility: Support for users with varying levels of technical expertise
Safety Design Features
- Lockout mechanisms to prevent accidental changes during critical procedures
- Clear visual indicators for alarm conditions and critical alerts
- Audit trails for tracking user actions and system changes
- Backup controls for critical functions
- Timeout features to prevent unauthorized access
Cleaning and Disinfection
Medical device touchscreens require frequent cleaning and disinfection to prevent healthcare-associated infections. Touchscreen materials and coatings must withstand harsh cleaning agents.
Cleaning Requirements
- Chemical Resistance: Compatibility with alcohol-based cleaners, quaternary ammonium compounds, and bleach solutions
- Frequent Cleaning: Ability to withstand multiple cleanings per day without degradation
- Sealed Design: Protection against liquid ingress into device internals
- Anti-Microbial Coatings: Optional coatings to reduce bacterial growth
- Easy Maintenance: Smooth surfaces without crevices that trap contaminants
Future Trends in Medical Touchscreen Technology
The future of touchscreen technology in medical devices includes several emerging trends that will further enhance usability and functionality.
- Haptic Feedback: Advanced tactile feedback for better user confirmation and reduced errors
- Gesture Recognition: Air gestures and proximity detection to reduce surface contact
- Voice Integration: Combined touch and voice control for hands-free operation
- AI-Powered Interfaces: Intelligent interfaces that adapt to user preferences and workflow patterns
- Flexible Displays: Bendable and foldable touchscreens for new medical device form factors
- Enhanced Durability: Improved resistance to chemicals, impacts, and wear
- Better Glove Compatibility: Advanced touch technologies that work reliably with all glove types
Implementation Best Practices
Successful implementation of touchscreen technology in medical devices requires careful planning and consideration of clinical workflows.
Implementation Steps
- Needs Assessment: Understand clinical workflows and user requirements
- Technology Selection: Choose appropriate touchscreen technology based on application needs
- User Testing: Conduct usability testing with actual healthcare providers
- Training Programs: Develop comprehensive training for end users
- Integration Planning: Ensure compatibility with existing systems and workflows
- Maintenance Planning: Establish cleaning protocols and maintenance schedules
Touchscreen technology has become an essential component of modern medical devices, transforming how healthcare professionals interact with complex medical equipment. From patient monitoring to surgical systems, touch interfaces improve usability, enhance workflow efficiency, and contribute to better patient care outcomes.
The unique requirements of medical environments—including gloved operation, frequent disinfection, and regulatory compliance—demand careful selection and implementation of touchscreen technology. By understanding these requirements and following best practices, healthcare facilities can successfully integrate touchscreen interfaces that enhance clinical workflows while maintaining patient safety.
As touchscreen technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated interfaces that further improve the usability and effectiveness of medical devices, ultimately contributing to better healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.